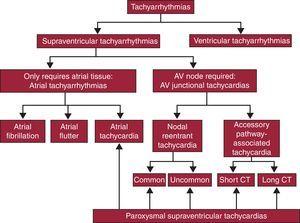
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia Arises From Which Form of Reentry
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia PSVT is defined as a regular rapid heart beat which initiates and terminates suddenly. Blood tests may be done to rule out specific underlying causes such as hyperthyroidism or electrolyte abnormalities.
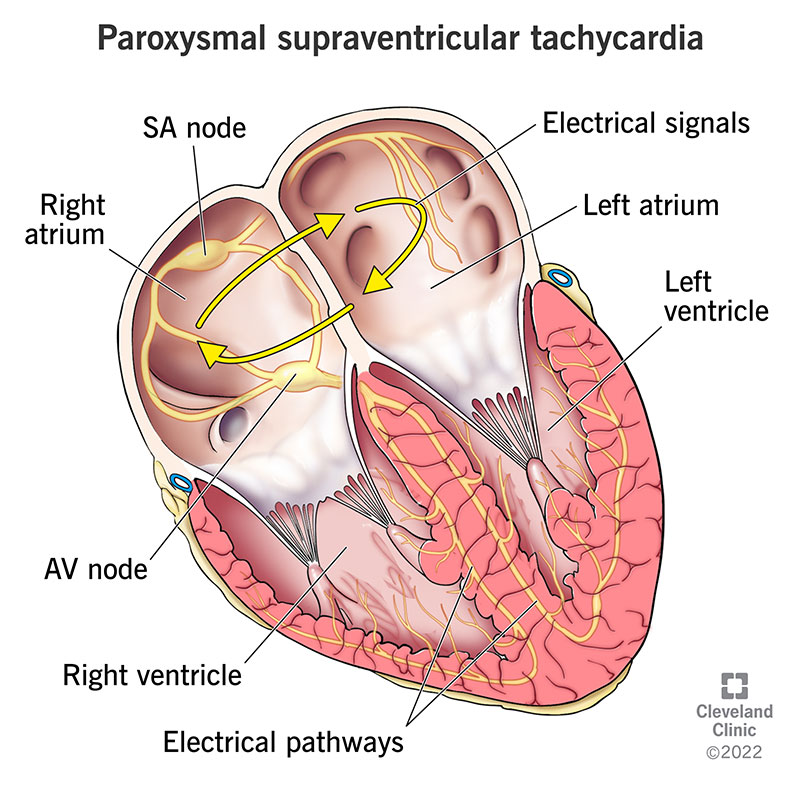
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia Psvt Causes Symptoms
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia Hakan Oral Fred Morady Supraventricular tachycardias arise in or involve at least some part of the atrium or atrioventricular junction.
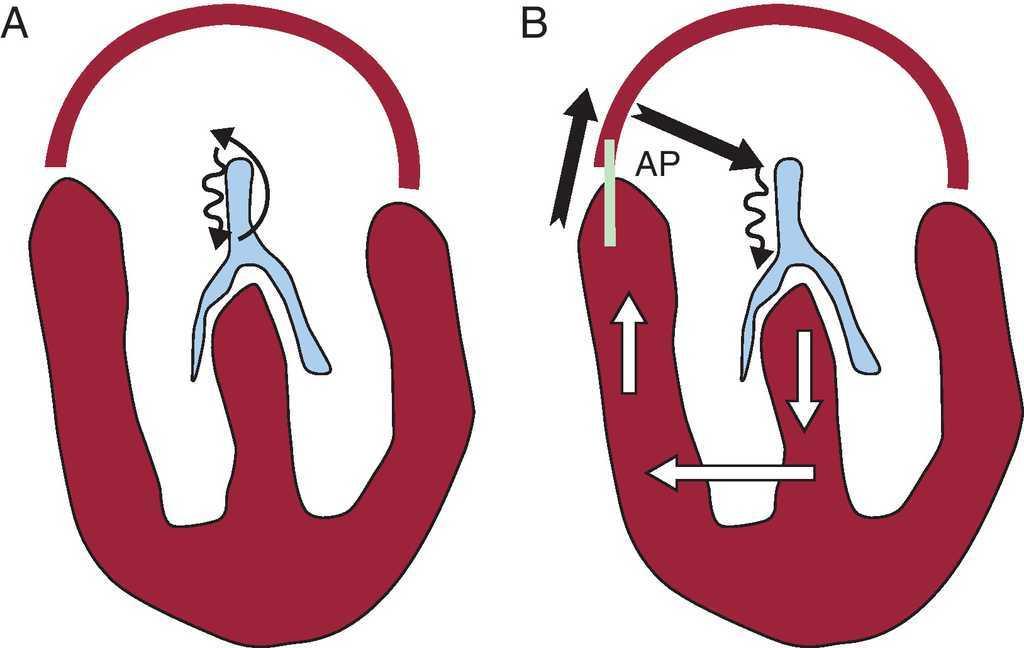
. The reentry pathway see figure Mechanism of typical reentry in supraventricular tachycardia is within the Atrioventricular AV node about 50 Accessory bypass tract 40 Atria or sinoatrial SA node 10 AV nodal reentrant tachycardia occurs most often in otherwise healthy patients. The cause is not known. Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia PSVT is a tachydysrhythmia average heart rate 160220 bpm initiated and sustained by tissue at or above the AV node.
PSVT is most common in younger subjects with normal hearts Risk factors Smoking caffeine stress alcohol abuse overactive thyroid excess thyroid hormone intake drugseg digitalis. The most common cause of paroxysmal SVT. Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia PSVT is usually caused by an atrioventricular AV nodal reentrant circuit and rarely by an auxiliary AV bypass tract Wolff-Parkinson-White WPW syndrome.
Currently there are various possible treatments going from medicines such as adenosine and beta-blockers to cardioversion. The phrase paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia describes a group of arrhythmias with similar electrocardiographic features but different mechanisms that have been clarified in recent years with specialized intracardiac recording and pacing techniques. Often people have no symptoms.
Diagnosis is typically by electrocardiogram ECG holter monitor or event monitor. Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia have their origin above the His bundle. HR 120-250 bpm AV nodal reentrant tachycardia AVNRT.
It is most commonly triggered by an atrial premature beat. Atrioventricular accessory pathways macro reentry. The accessory atrioventricular pathways are the most frequent cause of supraventricular tachycardia in paediatric age and give rise to atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia AVRT.
Properties of the focal atrial tachycardia Focal AT. A normal heart rate is 60 to 100 beats per minute. The rapid heartbeat may last a few seconds or many hours.
WolffParkinsonWhite WPW syndrome is a rare abnormal condition frequently associated with paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia PSVT and is described as an arrhythmia under the form of increased heartbeat. Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia Supraventricular tachycardia Cardiology Tachycardia triggered sporadically in the myocardium above the ventricles. In five patients studied A-V conduction time and refractory periods were normal but atrial premature depolarizations APD within a.
Healthy young individuals middle age and WOMEN. AVNRT is diagnosed in 50-60 of patients who present with regular narrow QRS tachyarrhythmia and is often in. The most common supraventricular tachycardia is the atrioventricular nodal re-entry tachycardia.
Synchronized electrical cardioversion is the treatment of choice for patients with evidence of hemodynamic instability eg systolic blood pressure. Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia PSVT is a type of supraventricular tachycardia named for its intermittent episodes of abrupt onset and termination. They are generally due to one of two mechanisms.
PSVT can be a form of a re-entry. With any mechanism of the occurrence of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia extrasystole develops beforehand. Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia most commonly arises from reentry within the atrioventricular AV node.
SART is a form of paroxysmal SVT characterized by palpitations and tachycardia rates slower than AVNRT or AVRT typically ranging from 100 to 150 beatsmin. In paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia abnormal conduction of that electricity causes the atrium and secondarily the ventricles to beat very rapidlyIt is referred to as paroxysmal because the rapid rate can occur sporadically and without warning and may also stop on its own. It is most commonly triggered by an atrial premature beat.
AV nodal reentrant tachycardia. PSVT may have a variety of electrophysiologic mechanisms including atrial tachycardia atrioventricular AV nodal reentry and tachycardia involving an accessory AV connection. Re-entry or increased automaticity.
AV nodal reentrant tachycardia a paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia - most common form of PSVT - it is due to reentry around teh AV node and surrounding transitional zone - the atria and ventricles are activated at approximately the same time process. 46 Most had organic heart disease. Notes on Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia PATFocal Atrial Tachycardia Focal AT Focal atrial tachycardia is caused by enhanced automaticity or re-entrant circuits giving rise to a flutter like atrial and consequently ventricular tachycardia.
46 Gomes reported a history of recurrent palpitations with a significant proportion having syncope or dizzy spells. Otherwise symptoms may include palpitations feeling lightheaded sweating shortness of breath and chest pain. However this definition has a historical origin and is imprecise regarding AV-reentry tachycardia using an accessory pathways since this tachycardia use the ventricule a part of the reentry-circuit.
Supraventricular tachycardias develop as a result of abnormal automaticity triggered activity or most commonly reentry. Most do not have structural heart disease prognosis of PSVT heart failure pulmonary edema myocardial ischemia andor myocardial infarction. One of the common causes of paroxysmal SVT is AVNRT.
W regular narrow QRS tachyarrhythmia. His bundle recordings during spontaneous and induced episodes of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia SVT demonstrated that the site of reentry responsible for this arrhythmia was in the A-V node. It is estimated there will be approximately.
The reentry pathway see figure Mechanism of typical reentry in supraventricular tachycardia is within the Atrioventricular AV node about 50 Accessory bypass tract 40 Atria or sinoatrial SA node 10 AV nodal reentrant tachycardia occurs most often in otherwise healthy patients. Reentry accounts for most cases and has been. Unlike sinus tachycardia PSVT usually begins and ends abruptly.
Extrasystolia is the most common form of arrhythmia which manifests itself in the form of disturbance of the heart rhythm and is characterized by the occurrence of single or paired premature contractions of the heart. The incidence of PSVT in the US population is 225 per 1000 persons. On the other hand children have a much lower incidence than adults of atrioventricular nodal reentrant.

Supraventricular Tachycardia An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
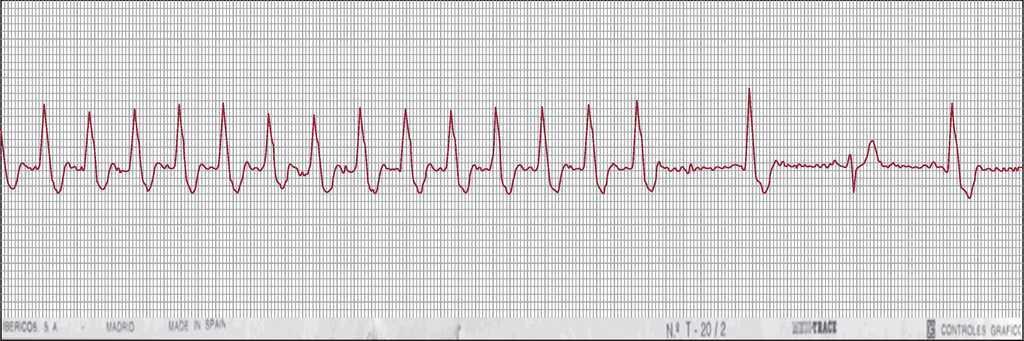
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardias And Preexcitation Syndromes Revista Espanola De Cardiologia
Supraventricular Tachycardia Wikiwand

Reentrant Supraventricular Tachycardias Svt Including Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome Cardiovascular Disorders Msd Manual Professional Edition

Supraventricular Tachycardias Rcemlearning

Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia Psvt Johns Hopkins Medicine

Supraventricular Tachycardia An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Supraventricular Tachycardia Mechanisms Diagnosis Management Ppt Video Online Download

Supraventricular Tachycardia Ppt Download
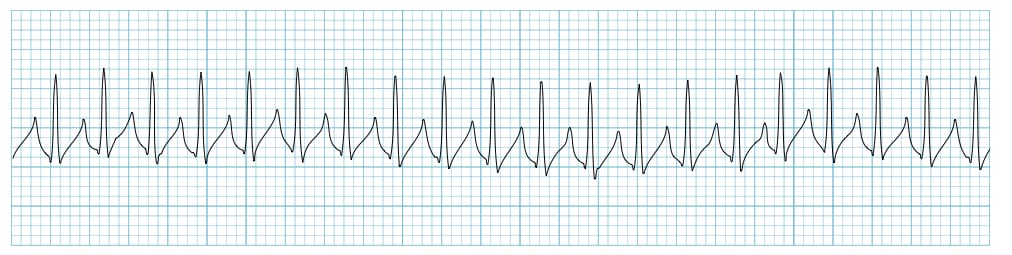
Supraventricular Tachycardia Svt Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis

The Supraventricular Tachycardias Proposal Of A Diagnostic Algorithm For The Narrow Complex Tachycardias Journal Of Cardiology
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardias And Preexcitation Syndromes Revista Espanola De Cardiologia
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardias And Preexcitation Syndromes Revista Espanola De Cardiologia

Common Types Of Supraventricular Tachycardia Diagnosis And Management American Family Physician

References In Supraventricular Arrhythmias Clinical Framework And Common Scenarios For The Internist Mayo Clinic Proceedings

References In Supraventricular Arrhythmias Clinical Framework And Common Scenarios For The Internist Mayo Clinic Proceedings

Comments
Post a Comment